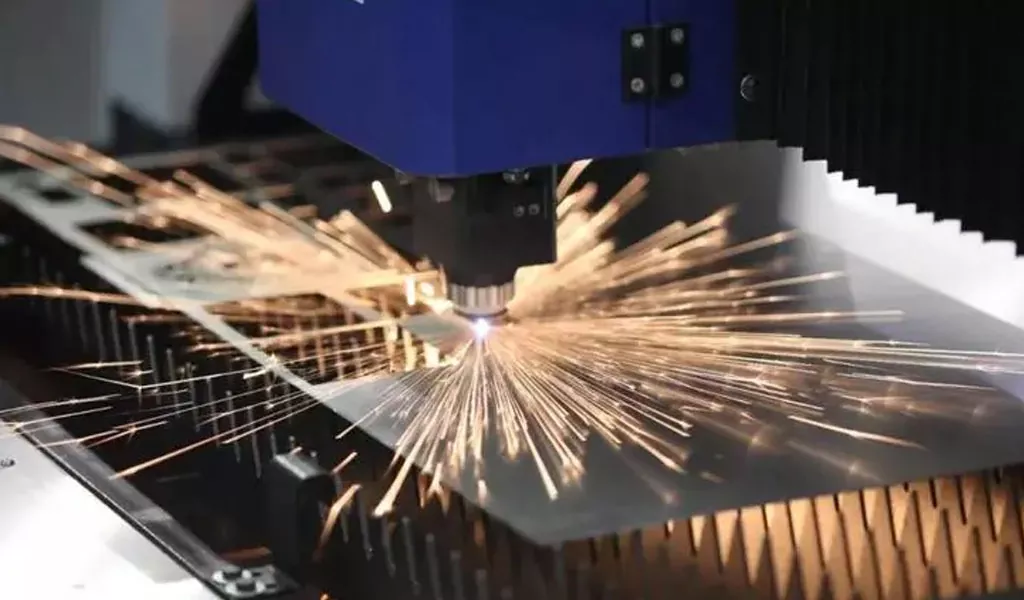
In the current sheet fabrication industry, laser cutting machines are commonly used for processing. Because laser cutting machines are efficient and flexible, they can solve the inconvenience caused by traditional CNC punch machines. The laser cutting machine adopts a non-contact processing solution, which has the remarkable characteristics of no mechanical stress and deformation, simple operation, high cutting accuracy, and small heat-affected zone.
Laser cutting is the most important application technology in the laser processing industry, accounting for more than 70% of the entire laser processing industry. Laser cutting is currently the most advanced cutting technology in the world. Because it has the advantages of precision manufacturing, flexible cutting, special-shaped processing, one-time molding, high speed and high efficiency, it solves many problems that cannot be solved by conventional methods in industrial production. Lasers can cut most metallic and non-metallic materials.
What Is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting uses a high-energy-density laser beam to heat the workpiece, causing the temperature to rise rapidly and reach the boiling point of the material in a very short time. The material begins to vaporize and form steam. These vapors are ejected at high speed while creating cuts in the material.
Stainless steel below 4mm can be cut with laser cutting equipment, and carbon steel with a thickness of 20mm can be cut with laser beam and oxygen, but a thin oxide film will be formed on the cutting surface after adding oxygen.
Since there are no tooling costs, laser cutting equipment is also suitable for producing low-volume parts in a variety of sizes that were previously impossible to machine.
Laser cutting equipment typically uses computer numerical control (CNC) units, which can then receive cutting data from a computer-aided design (CAD) workstation via a telephone line.
The principle of laser cutting is to use a focused high-power density laser beam to irradiate the workpiece, causing the irradiated material to quickly melt, vaporize, ablate or reach the ignition point. At the same time, a high-speed airflow coaxial with the beam blows away the molten material, cutting the workpiece. Laser cutting is one of the thermal cutting methods.
Characteristics Of Laser Cutting Technology
- High precision. The positioning accuracy is 0.05mm and the repeat positioning accuracy is 0.02mm.
- The slit is narrow. The laser beam is focused into a very small spot, reaching a very high power density at the focus, and the material is heated to the point of vaporization and evaporates to form holes. As the beam moves linearly relative to the material, the holes continuously form slits with a very narrow width. The incision width is generally 0.10-0.20ram.
- The cutting surface is smooth. There are no burrs on the cutting surface, and the surface roughness of the cutting is generally controlled within Ral2.5;A.
- high speed. The cutting speed can reach 10m/min, and the maximum positioning speed can reach 70m/m/n, which is much faster than wire cutting.
- Cutting quality is good. Non-contact cutting, the cutting edge is very little affected by heat, there is basically no thermal deformation of the workpiece, and the sagging formed during punching and shearing of the material is completely avoided, and the cutting seam generally does not require secondary processing.
- No damage to the workpiece. The laser cutting head will not come into contact with the material surface, ensuring that the workpiece will not be scratched.
- Not affected by the hardness of the material being cut. Laser can process steel plates, stainless steel, aluminum alloy plates, carbide, etc., and can perform deformation-free cutting regardless of hardness.
- Not affected by the shape of the workpiece. Laser processing is very flexible, can process any graphics, and can cut pipes and other special-shaped materials.
- Can cut non-metals. Such as plastic, wood, PVC, leather, textiles and plexiglass, etc.
- Save mold investment. Laser processing does not require molds, has no mold consumption, does not need to repair molds, and saves the time of replacing molds, thus saving processing costs and reducing production costs. It is especially suitable for the processing of large products.
- Save materials. Using computer programming, products with different shapes can be nested across the board to maximize material utilization.
- The new product manufacturing cycle is shortened. For trial production of new products, the quantity is small, the structure is uncertain and may be changed at any time, and the mold cannot be produced at all. The laser cutting machine greatly shortens the manufacturing cycle of new products and reduces mold investment.
Classification Of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting can be divided into four categories: laser vapor cutting, laser melting cutting, laser oxygen cutting and laser scribing and controlled fracture.
1) Laser Vapor Cutting
A high-energy-density laser beam is used to heat the workpiece, causing the temperature to rise rapidly, reaching the boiling point of the material in a very short time, and the material begins to vaporize to form steam. These vapors are ejected at high speed while creating cuts in the material. Generally, the vaporization heat of materials is very large, so laser vaporization cutting requires large power and power density.
Laser vapor cutting is mainly used to cut extremely thin metal materials and non-metal materials (such as paper, cloth, wood, plastic and rubber, etc.).
2) Laser Melting And Cutting
During laser cutting, the metal material is melted by laser heating, and then non-oxidizing gas (Ar, He, N, etc.) is sprayed through a nozzle coaxial with the beam, and the liquid metal is discharged by the strong pressure of the gas to form a cut. Laser cutting does not require complete vaporization of the metal, and the energy required is only 1/10 of vaporization cutting.
Laser cutting is mainly used to cut some materials or reactive metals that are not easily oxidized, such as stainless steel, titanium, aluminum and their alloys.
3) Laser Oxygen Cutting
The principle of laser cutting is similar to oxyacetylene cutting. It uses laser as preheating heat source and active gas such as oxygen as cutting gas. On the one hand, the blown gas reacts with the cutting metal, causing an oxidation reaction and releasing a large amount of oxidation heat; on the other hand, the molten oxide and melt are blown out of the reaction zone, forming a gap in the metal. Since the oxidation reaction during the cutting process generates a large amount of heat, the energy required for laser oxygen cutting is only 1/2 of that of melting cutting, and the cutting speed is much faster than laser vapor cutting and melting cutting. Laser cutting is mainly used for easily oxidized metal materials such as carbon steel, titanium steel, and heat-treated steel.
4) Laser Scribing And Fracture Control.
Laser scribing uses a high-energy-density laser to scan the surface of a brittle material, causing the material to heat and evaporate into small grooves. Then a certain amount of pressure is applied, and the brittle material will crack along the small grooves. Lasers used for laser scribing are generally Q-switched lasers and CO2 lasers.
Fracture control uses the steep temperature distribution generated by laser grooves to generate local thermal stress in brittle materials, causing the material to fracture along the small grooves.
Laser Cutting Application Range
Most laser cutting machines are controlled by CNC programs or made into cutting robots. As a precision processing method, laser cutting can cut almost all materials, including two-dimensional or three-dimensional laser cutting of metal sheets.
In the field of automobile manufacturing, cutting technology of spatial curves such as roof windows has been widely used. BE-CU Prototype uses a 500W laser to cut complex body panels and various curved parts. In the aerospace field, laser cutting technology is mainly used to cut special aerospace materials, such as titanium alloy, aluminum alloy, nickel alloy, chromium alloy, stainless steel, beryllium oxide, composite materials, plastics, ceramics and stainless steel. Aerospace parts processed by laser cutting include engine flame tubes, titanium alloy thin-walled casings, aircraft frames, titanium alloy skins, wing stringers, tail panels, helicopter main rotors, space shuttle ceramic insulation tiles, etc.
Laser cutting and forming technology is also widely used in the field of non-metallic materials. It can not only cut high hardness and brittle materials, such as silicon nitride, ceramics, stainless steel, etc. It can also cut and process flexible materials such as cloth, paper, plastic plates, rubber, etc. If you use laser to cut clothes, you can save 10% ~ 12% of clothes and increase the efficiency by more than 3 times.
